Hair Loss in Women: Hair Transplant Solutions and Alternatives

Hair Loss in Women: Hair Transplant Solutions and Alternatives
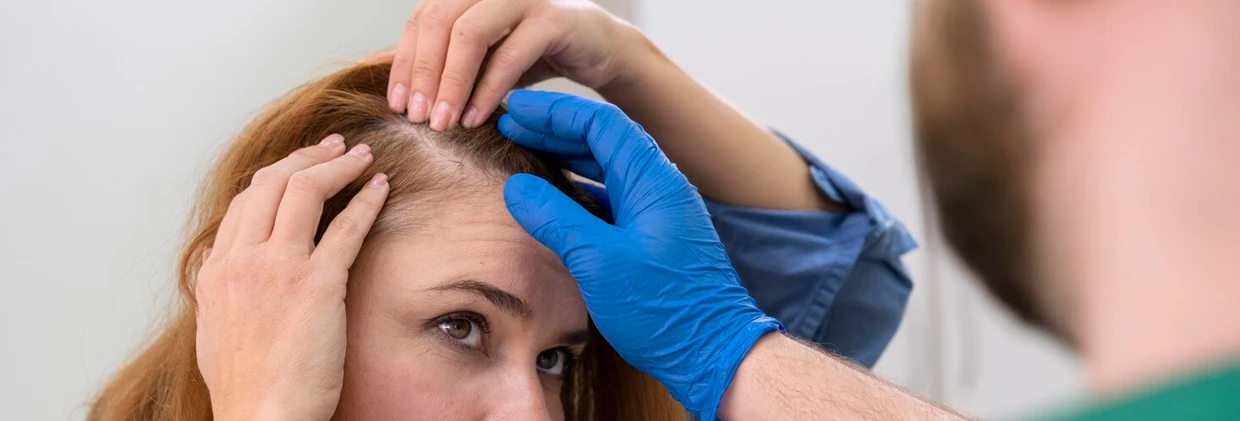
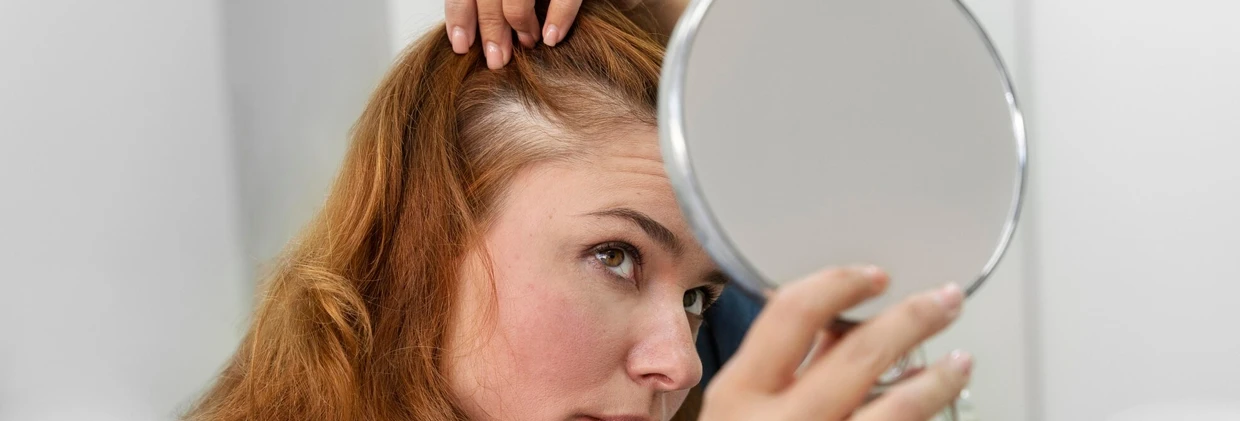
For women, hair loss is not just an aesthetic concern but a sensitive issue that deeply affects self-confidence and psychological well-being. Instead of the clear receding hairline seen in men, hair loss in women typically manifests as diffuse thinning across the entire crown area. This difference completely separates the treatment approach from that for men and magnifies the importance of accurate diagnosis. As the Görkem Kazan Hair Transplant clinic, we examine the complex causes of hair loss in women, detailing when hair transplantation is an appropriate solution and which effective non-surgical alternatives are available.
The first step in seeking a solution for hair loss in women should never be surgery; it should be a comprehensive diagnosis process to uncover the root cause of the shedding. The cause of the loss might be hormonal, nutritional, or stress-related. Unfortunately, a hair transplant performed without resolving this underlying issue will not lead to permanent success. Therefore, the correct treatment plan always begins with a multidisciplinary approach.
Main Causes and Types of Hair Loss in Women
Hair loss in women is generally evaluated using the Ludwig Classification and results from different biological processes than in men:
Main Causes
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like thyroid disorders, menopause, changes in birth control pills, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), and the post-pregnancy period (telogen effluvium) are the most common causes of shedding.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in Iron (anemia), Ferritin, Zinc, Vitamin D, and B12 can halt or slow the hair growth cycle.
- Stress and Trauma: Diffuse shedding seen after severe illness, major surgery, or intense emotional stress (Telogen Effluvium) is usually temporary but requires supportive treatment.
- Genetic Predisposition: Female pattern genetic baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia) occurs due to hair follicles’ sensitivity to DHT, but it is seen as diffuse thinning rather than complete baldness, as in men.
Types of Shedding
Hair loss in women typically starts from the crown area and spreads outward, rather than the recession of the front hairline seen in men. This fact directly influences the surgical decision.
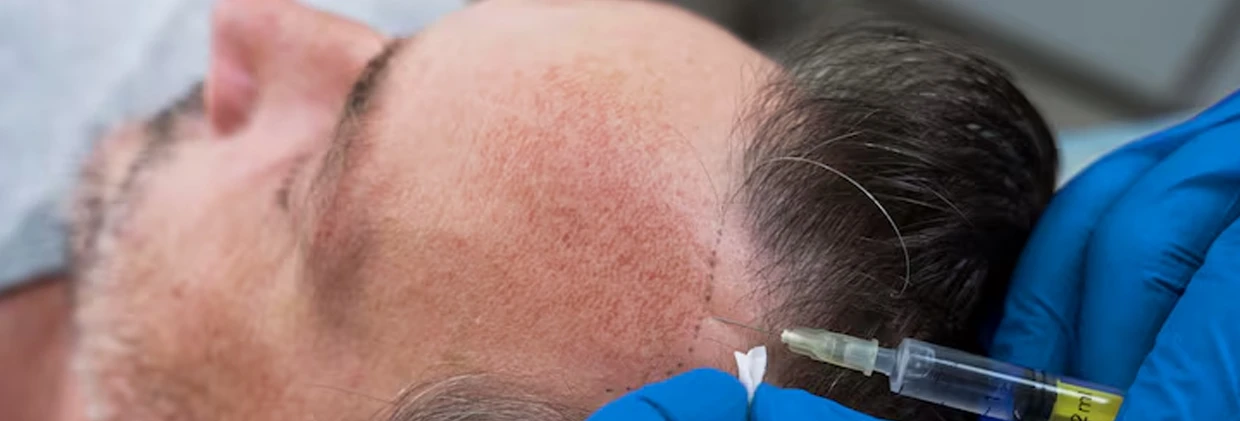
When is Hair Transplantation a Solution for Women?
Hair transplantation is not always the first option for women; however, it offers a permanent and excellent solution for specific types of hair loss:
- Localized Hair Loss (Scarring Alopecia): Hair loss only in a specific area due to accidents, burns, or surgical scars (including SCAR transplantation).
- Traction Alopecia: Permanent recession of the front hairline due to hair being pulled back tightly constantly (ponytails, braids). Since the follicles in this area are often dead, transplantation is the only solution.
- Congenitally High Forehead: Even without hair loss, to aesthetically lower the hairline and balance facial proportions.
- Cases with a Clear Donor Area: Most importantly, in rare situations where hair loss is confined to the recipient area, but the donor hairs on the back of the neck remain healthy, dense, and DHT-resistant.
Unsuitable Situation: In cases of diffuse thinning across the entire scalp (diffuse alopecia), which is most common in women, the donor area is also likely thinned and weakened; consequently, the transplanted grafts would not be permanent. In this scenario, non-surgical alternatives must be the priority.
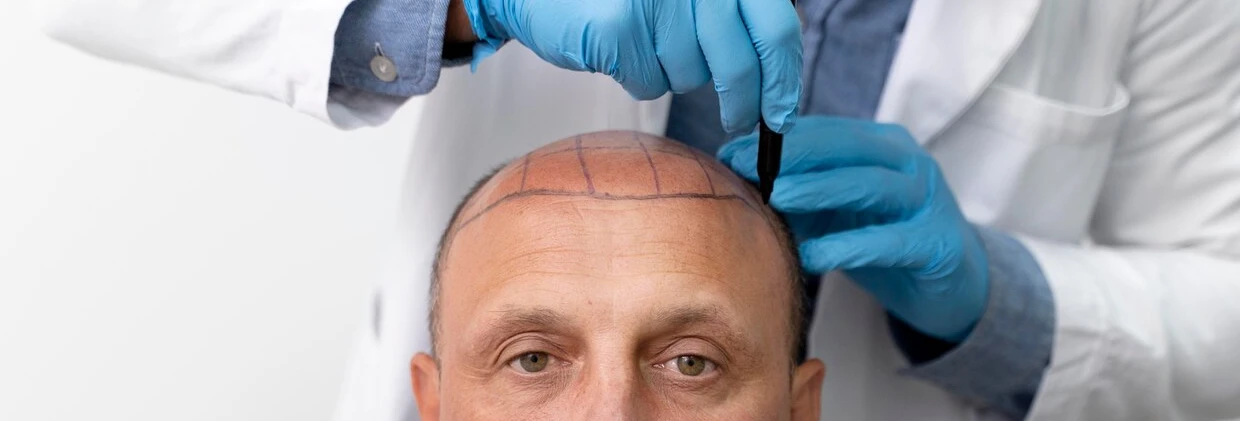
Techniques Applied in Women: Unshaven DHI and FUE
Since the majority of female patients do not want to cut their hair short, operations are usually planned as Unshaven DHI or Partial Shaven FUE. The DHI technique, in particular, is preferred by female patients because it allows for dense implantation between existing hairs.
Non-Surgical Alternative Treatments: Strengthening Hair Follicles
For the majority of female patients, the most effective solutions are regenerative treatments that nourish and revitalize weakened hair follicles:
1. PRP Therapy (Platelet-Rich Plasma)
PRP is considered the gold standard in treating female hair loss. Growth factors obtained from the patient’s own blood are injected directly into the hair follicles. This process:
- Thickens thinned hair strands and increases hair volume.
- Shortens the resting phase (telogen) and lengthens the growth phase (anagen).
- Improves scalp blood flow and nourishes the follicles.
PRP is particularly successful in thinning caused by hormonal changes or stress-related shedding. For more detailed information on this topic, you can review our PRP and Mesotherapy page.
2. Stem Cell and Exosome Treatments
Stem cell and exosome treatments, the next level above PRP, are the most current biological solutions for reducing the severity of shedding and improving hair quality in women. “Messengers” (exosomes) derived from stem cells send direct repair signals to weakened follicles, encouraging them to regain strength. This provides long-term protection and densification. For more information, please see our stem cell and exosome treatments page.
3. Medication and Supplement Treatments
- Minoxidil: Used topically (usually 2% or 5%), Minoxidil stimulates hair growth by increasing blood flow to the scalp. However, it must be used long-term and under a doctor’s supervision.
- Nutritional Supplements: Deficiencies in Iron (Ferritin), Zinc, Biotin, and Vitamin D, detected by blood tests, must be corrected with supplements. Without addressing these deficiencies, no amount of PRP or transplantation can achieve full success. Sources like the National Library of Medicine (NCBI) emphasize the direct relationship between nutritional deficiencies and hair health.
The Importance of Diagnosis for Successful Treatment
The biggest mistake made when starting treatment for hair loss in women is the failure to accurately determine the cause. Hair loss is a symptom, not a disease. Therefore, an accurate diagnosis constitutes 90% of the success:
- Blood Tests: Thyroid function tests, complete blood count (especially Ferritin and Hemoglobin), hormone levels, and vitamin levels must be checked.
- Trichoscopy (Hair Analysis): This analysis, performed with a specialized device, shows the degree of hair follicle miniaturization, density, and viability. This determines whether you need surgery or regenerative therapy. It is important to schedule a hair analysis appointment for a comprehensive evaluation.
While hair transplantation can be a solution for certain types of female hair loss, the most effective results are often achieved with regenerative therapies. Starting the treatment from the right point and receiving support from the correct expertise are key to achieving lasting results. For a detailed diagnosis and a treatment plan tailored specifically to you, you can contact the specialists at Görkem Kazan Hair Transplant.